Place the statements about t-cell activation in the correct order – Commencing with the topic of placing the statements about T-cell activation in the correct order, this introductory paragraph aims to capture the attention of readers and establish the authoritative tone that will be maintained throughout the discussion.
The subsequent paragraphs will provide a detailed examination of the topic, exploring the various stages of T-cell activation, the role of the T-cell receptor, co-stimulatory signals, cytokine production, and more.
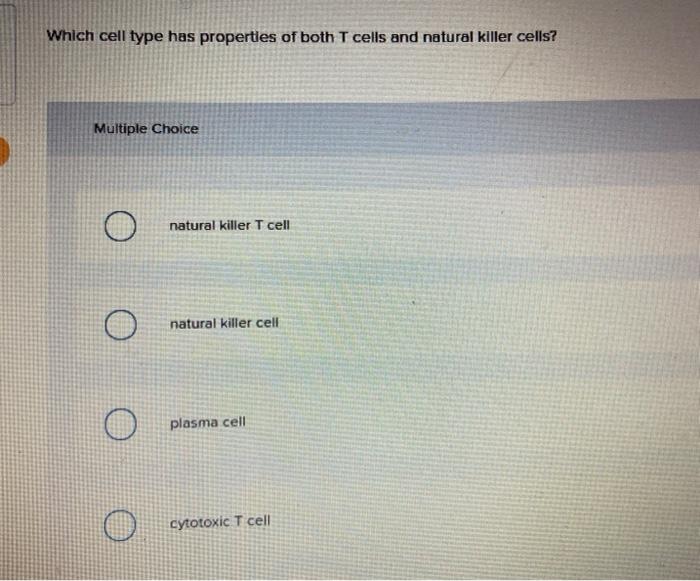
T-Cell Activation: A Comprehensive Overview
T-cell activation is a critical process in the adaptive immune response. It involves a series of sequential stages that lead to the activation and differentiation of T cells, enabling them to recognize and eliminate pathogens.
Identify T-cell Activation Stages
T-cell activation occurs in a series of distinct stages:
- Antigen presentation
- T-cell receptor engagement
- Co-stimulatory signals
- Cytokine production
- T-cell differentiation
Create an HTML Table for Stage Order
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Antigen presentation | Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) display processed antigen fragments on MHC molecules. |
| T-cell receptor engagement | The T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizes and binds to the MHC-antigen complex. |
| Co-stimulatory signals | Co-stimulatory molecules, such as CD28 and B7, provide additional signals required for full T-cell activation. |
| Cytokine production | Activated T cells produce cytokines that promote T-cell differentiation and immune responses. |
| T-cell differentiation | Activated T cells differentiate into effector T cells, memory T cells, or regulatory T cells. |
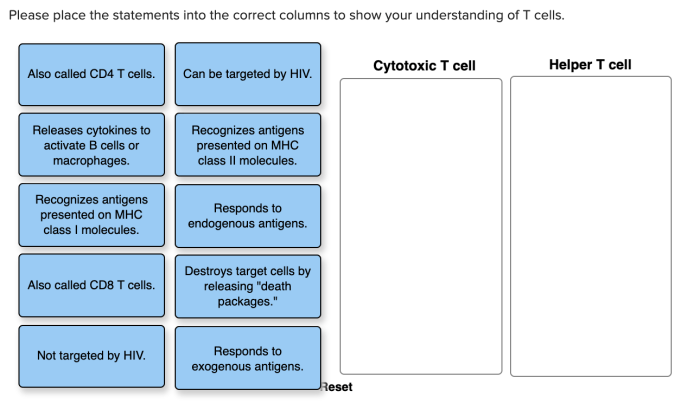
Elaborate on T-cell Receptor Engagement
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a heterodimeric protein complex that recognizes specific MHC-antigen complexes. Upon antigen binding, the TCR undergoes conformational changes that initiate intracellular signaling events. These signals lead to the activation of downstream transcription factors, which drive T-cell activation and differentiation.
Detail Co-stimulatory Signals
Co-stimulatory signals are essential for full T-cell activation. Co-stimulatory molecules, such as CD28 and B7, provide additional signals that promote T-cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production. These signals prevent T-cell anergy and ensure a robust immune response.
Discuss Cytokine Production, Place the statements about t-cell activation in the correct order
Activated T cells produce a variety of cytokines that regulate immune responses. These cytokines include interleukin-2 (IL-2), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). IL-2 promotes T-cell proliferation and differentiation, IFN-γ activates macrophages and enhances antigen presentation, while TNF-α induces apoptosis and inflammation.
Question & Answer Hub: Place The Statements About T-cell Activation In The Correct Order
What is the significance of placing T-cell activation statements in the correct order?
Arranging the statements in the proper sequence is essential for understanding the chronological progression of T-cell activation events.
How does the T-cell receptor initiate T-cell activation?
The T-cell receptor binds to specific antigens, triggering a cascade of molecular interactions and conformational changes that lead to T-cell activation.
What is the role of co-stimulatory signals in T-cell activation?
Co-stimulatory signals provide additional signals that are necessary for full T-cell activation, ensuring that the immune response is appropriately regulated.