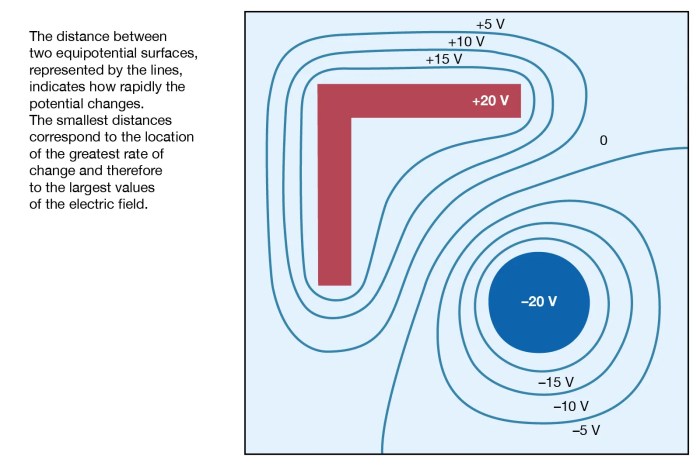
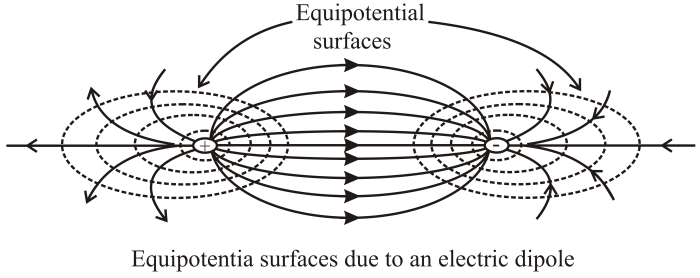
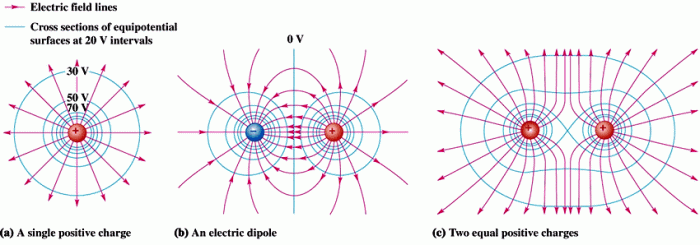
An equipotential surface that surrounds a point charge – In the realm of electrostatics, equipotential surfaces surrounding point charges emerge as fascinating entities that unveil the intricate interplay between electric potential and electric fields. These surfaces, defined by constant electric potential, offer a unique perspective on the behavior of electric charges and their influence on the surrounding space.
The shape and characteristics of equipotential surfaces surrounding point charges provide valuable insights into the distribution of electric fields. The distance from the point charge and the magnitude of the electric potential determine the shape and spacing of these surfaces, revealing the interplay between electric charge and electric potential.
1. Definition and Properties of Equipotential Surfaces: An Equipotential Surface That Surrounds A Point Charge
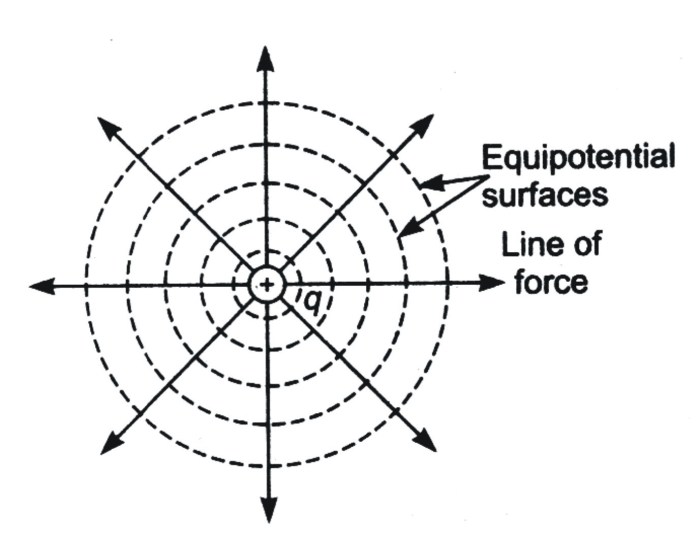
An equipotential surface is a surface in space where the electric potential is constant. This means that any point on an equipotential surface has the same electric potential as any other point on that surface.
Equipotential surfaces are perpendicular to electric field lines. This is because the electric field lines point in the direction of the greatest change in electric potential, and the change in electric potential is zero along an equipotential surface.
2. Equipotential Surfaces Surrounding a Point Charge
The equipotential surfaces surrounding a point charge are spherical shells. The radius of each shell is proportional to the square root of the electric potential on that shell.
The electric field lines surrounding a point charge are radial. This means that they point directly away from the point charge. The electric field is strongest near the point charge and weakest far away from it.
3. Applications of Equipotential Surfaces
Equipotential surfaces are used in a variety of applications, including electrostatics and electrical engineering.
- In electrostatics, equipotential surfaces are used to map the electric field around a charged object.
- In electrical engineering, equipotential surfaces are used to design and analyze electrical systems.
Equipotential bonding is a technique used to connect different parts of an electrical system to the same electrical potential. This helps to prevent electrical shocks and fires.
4. Mathematical Representation of Equipotential Surfaces, An equipotential surface that surrounds a point charge
The equation for an equipotential surface surrounding a point charge is:
“`V = kQ/r“`
where:
- V is the electric potential on the equipotential surface
- k is Coulomb’s constant
- Q is the charge of the point charge
- r is the distance from the point charge to the equipotential surface
This equation can be used to determine the shape and properties of equipotential surfaces surrounding a point charge.
Detailed FAQs
What is an equipotential surface?
An equipotential surface is a surface where every point has the same electric potential. It is perpendicular to the electric field lines at each point.
What is the relationship between electric potential and equipotential surfaces?
The electric potential is constant on an equipotential surface. The potential difference between two equipotential surfaces is equal to the work done in moving a charge between the surfaces.
What are the applications of equipotential surfaces?
Equipotential surfaces are used in a variety of applications, including the design of electrical systems, the analysis of electric fields, and the study of electrostatics.